A chemical filter is a means of removing dissolved wastes in a liquid. These filters help by removing contaminants in a liquid. For example, chemical filters are used to purify water for dialysis patients. Read More…
Liquid filters are just a part of our complete line of filters and cartridges. Shelco is dedicated to providing our customers with excellent quality customer service and high quality products. This is shown through our state-of-the-art research and development team working to increase performance while reducing costs. We take pride in the fact that Shelco filters are distributed and used all over ...

Clean Liquid Systems is a leading manufacturer of air and liquid filters. Our number one priority is to create the best filters that match the needs of our customers. We strive to have a fast turnaround while not reducing the quality of our products. Filtration is the only thing we do and ensure that we make our products right. We provide our customers with hundreds of years of experience and...
At Great Lakes Filters, we specialize in providing advanced liquid filtration solutions that keep industrial systems running clean, efficient, and reliable. With decades of experience in the filtration industry, we have developed a deep understanding of how to meet the demanding requirements of diverse applications—from metalworking fluids and coolants to chemical processing, water treatment,...
At Ryan Herco Flow Solutions, we are dedicated to providing high-quality liquid filtration products that keep critical processes running smoothly. Our expertise lies in helping customers solve complex fluid management challenges, and our liquid filters are at the heart of those solutions.
More Chemical Filter Manufacturers

What are Chemical Filters?
Chemical filters are essential devices engineered to separate, remove, or neutralize specific chemical contaminants from liquids or gases, ensuring cleaner, safer, and more efficient processes across a broad spectrum of industries. The term "chemical filter" encompasses a diverse array of filtration technologies, including but not limited to liquid filters, hydraulic filters, industrial water filters, biodiesel filters, and gas filtration systems. In the context of liquid filtration, chemical filters play a crucial role in protecting equipment, improving product purity, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
One of the most widely recognized types of chemical filters is the carbon filter. Carbon filtration is fundamental in both residential and industrial water purification applications, where it effectively removes chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, and other chemical contaminants. Home water filters typically focus on improving taste, odor, and aesthetic quality, while industrial water filtration systems are designed to achieve rigorous purity standards for laboratory, pharmaceutical, or manufacturing processes.
In addition to water filtration, chemical filters encompass a range of liquid and gas filtration products designed for various applications. For example, gas filters are vital in removing particulate and chemical impurities from fuel, preventing sediment buildup and ensuring optimal engine performance in vehicles and industrial machines. Likewise, hydraulic filters protect sensitive hydraulic systems by removing metal shavings, dirt, and chemical contaminants from hydraulic fluid, thereby extending equipment life and reducing maintenance costs. Hydraulic filter solutions are indispensable in the construction, aerospace, and manufacturing sectors.
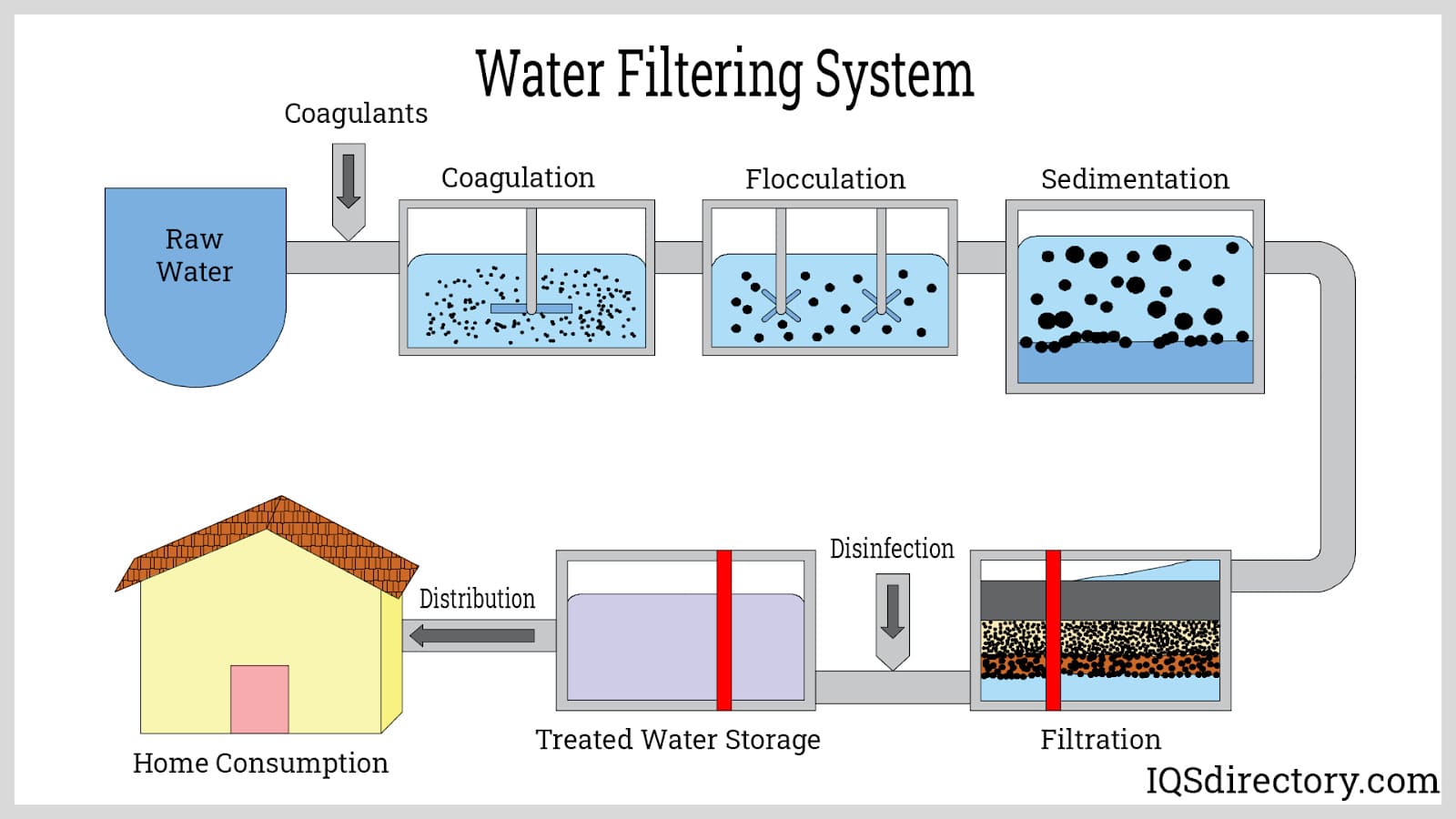
All liquid chemical filtration systems are engineered to extract undesirable particles or dissolved substances from a flowing liquid stream. This not only safeguards human health—by removing toxic elements such as fluoride, heavy metals, or chloramines—but also protects sensitive industrial equipment from corrosive or abrasive contaminants. The effectiveness of chemical filters largely depends on a combination of sound mechanical design and advanced filter media selection, such as activated carbon, ceramic, resin, or membrane materials.
One critical factor influencing a filter’s performance is flow rate. As filtration speed increases, the contact time between the fluid and the filter media decreases, often resulting in reduced contaminant removal. Conversely, slower flow rates typically enhance the degree of purification, making flow control an important consideration in the selection and design of chemical filtration systems.
How Do Chemical Filters Work?
Chemical filters operate by leveraging various physical and chemical processes to remove contaminants from fluids or gases. The primary mechanisms include adsorption (as seen in carbon filters), absorption, ion exchange, and mechanical filtration. For example, activated carbon filters rely on adsorption, in which dissolved chemicals are attracted to and held on the surface of the porous carbon granules. Other filters may utilize resin beds to exchange unwanted ions for harmless ones, or membranes with specific pore sizes to physically block particulates and pathogens.
Choosing the right chemical filter depends on the type of contaminants present, the desired purity level, and the application—whether for potable water, process fluids, laboratory solutions, or air purification. For those seeking to understand which chemical filter is right for your needs, ask yourself: What contaminants must be removed? What is the flow rate of your system? What are the regulatory or industry standards you must meet?
Types of Chemical Filters
Chemical filters come in many varieties, each optimized for specific contaminants, flow rates, and use cases. Here are the most common and effective types of chemical filters used in both residential and industrial settings:
Granular Activated Carbon (GAC) Filters
Granular activated carbon filters are among the most widely used and versatile chemical filters. They are exceptionally effective at removing chlorine, pesticides, herbicides, and a wide range of organic contaminants from water. Manufactured from natural carbon-rich materials like coconut shells, wood, or coal, GAC filters are treated to create a highly porous structure, maximizing their surface area for adsorption.

GAC filters are commonly used in both point-of-entry (whole house) and point-of-use (under-sink or countertop) water filtration systems. Their high adsorption capacity enables them to efficiently remove taste and odor-causing compounds, VOCs, and certain heavy metals. These filters are often backwashable, allowing for extended service life and cost-effective operation in high-volume applications. In industrial settings, GAC filters are integrated into pretreatment systems for reverse osmosis units or as final polishing filters for pharmaceutical and food production lines.
Catalytic Carbon Filters
While standard GAC filters excel at removing many organic chemicals, they are less effective against certain disinfectants like chloramines. Catalytic carbon filters are engineered to address this shortcoming. Catalytic carbon is a modified form of activated carbon, often derived from coconut shells, with a unique electronic structure that enhances its ability to break down chloramines and other persistent chemicals.
Chloramines, used by many municipal water treatment plants as an alternative to chlorine, can be harmful to aquarium life, plants, and individuals with certain health conditions, such as dialysis patients. Catalytic carbon filters are now the preferred solution for homes and businesses seeking to eliminate chloramines from their water supply. Like GAC filters, these systems require periodic backwashing and media replacement, but they offer superior performance in environments where chloramine contamination is a concern.

Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems
Reverse osmosis is a highly advanced chemical filtration method that uses a semipermeable membrane to separate dissolved ions, molecules, and larger particles from water. RO systems are widely recognized for their ability to remove an extensive range of contaminants, including bacteria, viruses, heavy metals, nitrates, sulfates, and dissolved salts. These systems are typically paired with pre-filters—such as GAC or catalytic carbon filters—to extend membrane life by removing chlorine and organic fouling agents.
RO filtration is the technology of choice in applications requiring ultra-pure water, such as laboratory analysis, pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage production, and residential drinking water purification. For those considering upgrading their water purification processes, explore more about reverse osmosis water filters and how they can be integrated with other chemical filtration products for optimal results.
Ion Exchange Filters
Ion exchange filters are specialized chemical filters that use synthetic resins to exchange unwanted dissolved ions—such as calcium, magnesium, or heavy metals—for less problematic ions like sodium or hydrogen. These filters are most commonly found in water softening systems, where they prevent scale buildup in pipes and appliances, and in boiler feed water treatment for industrial facilities. Ion exchange filters are also effective in removing toxic metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium from drinking water.
Other Filtration Options and Hybrid Systems
While carbon and ion exchange filters are highly effective, they are often combined with other treatment technologies for comprehensive contaminant removal. For instance, ceramic filters provide excellent microbial filtration, while ultraviolet (UV) disinfection systems destroy bacteria and viruses that pass through chemical filters. Many advanced water treatment systems employ a multi-stage approach, integrating sediment filters, carbon filters, ion exchange resins, and RO membranes for maximum water quality assurance.
Key Applications of Chemical Filters
Chemical filters are indispensable across a wide range of industries and settings. Here are some common and specialized applications:
- Potable Water Treatment: Removing chlorine, chloramines, pesticides, heavy metals, and organic contaminants to produce safe drinking water.
- Pharmaceutical & Biotechnology: Purifying process water and solvents to meet stringent regulatory standards for drug manufacturing, research, and laboratory analysis.
- Chemical Processing: Separating and purifying chemicals such as dyes, pesticides, glycerine, silicic acid, and white carbon in manufacturing environments.
- Food & Beverage Industry: Filtering fruit juices, wine, vegetable oils, soft drinks, and other food-grade liquids to improve product quality, shelf life, and safety.
- Environmental Engineering: Treating mining wastewater, chemical plant effluents, domestic wastewater, and stormwater runoff to remove hazardous contaminants and comply with environmental regulations.
- Power Generation: Protecting turbines and boilers by removing dissolved and suspended solids from cooling water and feedwater systems.
- Automotive & Aerospace: Filtering hydraulic fluids, engine coolants, and fuels to reduce maintenance costs and improve equipment reliability.
- Aquarium & Aquaculture: Maintaining healthy aquatic environments by removing ammonia, nitrites, and other harmful chemicals.
Benefits and Advantages of Chemical Filters
Chemical filters offer a multitude of benefits for residential, commercial, and industrial users. Here are the primary advantages:
- Effective Contaminant Removal: Capable of targeting specific chemical, biological, and physical contaminants—including chlorine, chloramines, VOCs, heavy metals, and pathogens.
- Improved Water Quality: Enhances taste, odor, and clarity, ensuring water meets safety and regulatory standards for consumption or industrial use.
- Large Adsorptive Surface Area: Especially with activated carbon, filters offer extensive porous networks for maximum contaminant capture.
- Reusable & Long-Lasting: Many chemical filters, especially those with backwashing capability, have extended service lives and lower operational costs.
- Versatile Applications: Suitable for diverse tasks, from household drinking water purification to high-volume industrial chemical processing.
- Protects Equipment: Reduces wear and tear on pumps, valves, boilers, and process lines by removing abrasive or corrosive contaminants.
- Environmental Compliance: Helps companies meet environmental discharge limits and sustainability goals by eliminating hazardous substances before release.
- Customizable Solutions: Filters can be tailored to specific flow rates, contaminant loads, and operational requirements.
How to Select the Best Chemical Filter for Your Needs
Choosing the right chemical filter involves carefully evaluating your water or process fluid quality, contaminant profile, and operational requirements. Here are some key questions to guide your selection process:
- What contaminants are present? Identify whether you need to remove chlorine, chloramines, heavy metals, pesticides, organic compounds, or particulates.
- What is the expected flow rate and volume? Sizing your filter correctly ensures optimal performance and lifespan.
- What is the desired water quality or purity level? Consider whether your application requires potable water, ultrapure industrial water, or basic contaminant reduction.
- Are there regulatory or industry standards? Ensure the filter system meets local, state, or federal guidelines for water or air quality.
- What is your budget for installation and maintenance? Factor in initial cost, replacement media, energy usage, and ongoing service requirements.
- Is a single-stage or multi-stage system needed? Multi-stage filtration often delivers broader contaminant removal and redundancy.
If you are unsure which filter technology suits your needs, consider reaching out to a reputable chemical filter manufacturer or consulting with an expert in liquid filtration solutions. For tailored recommendations, request a site assessment or water analysis to pinpoint the optimal solution.
Maintenance and Longevity of Chemical Filters
Proper maintenance is essential to ensuring your chemical filter system delivers consistent, high-quality results over time. Here are some best practices:
- Scheduled Backwashing: For backwashable filters like GAC and catalytic carbon, regular backwashing removes accumulated contaminants and restores flow rates.
- Timely Media Replacement: Replace filter media based on manufacturer recommendations or when contaminant breakthrough is detected.
- Monitor Flow and Pressure: Watch for drops in flow rate or increases in pressure, which may signal clogging or media exhaustion.
- Routine System Inspections: Check for leaks, corrosion, or damage to filter housings and seals.
- Water Quality Testing: Periodically test filtered water to verify performance and regulatory compliance.
Wondering how to extend the life of your chemical filter system? Explore our filter media options or reach out for maintenance tips and troubleshooting assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions About Chemical Filters
- How often should I replace my chemical filter? Replacement intervals vary depending on filter type, contaminant load, and water usage. Most manufacturers provide guidelines for optimal performance.
- Can chemical filters remove bacteria and viruses? Some filters, like RO membranes and ceramic filters, can remove microorganisms, but additional disinfection (e.g., UV) may be necessary for complete protection.
- What is the difference between mechanical and chemical filtration? Mechanical filters primarily remove suspended solids, while chemical filters target dissolved contaminants through adsorption, absorption, or ion exchange.
- Is it necessary to use multiple types of filters? For comprehensive contaminant removal, multi-stage filtration systems combining sediment, carbon, and specialty filters are often recommended.
- How do I know which filter size I need? Consult with a manufacturer or use flow rate calculators to determine the appropriate size based on your application and water quality.
Choosing the Correct Chemical Filter Manufacturer
To ensure the best results when purchasing a chemical filter, it’s essential to select a reputable chemical filter manufacturer with proven expertise and a track record of quality products. Compare at least four manufacturers using our curated list of chemical filter suppliers. Each manufacturer’s profile page highlights their specialties, certifications, and capabilities, along with a direct contact form to request more information or a customized quote.
Ready to start your search? Review each chemical filter company website using our proprietary previewer to evaluate their offerings, customer reviews, and industry focus. Then, leverage our simple RFQ form to contact multiple chemical filter manufacturers and receive competitive quotes tailored to your application.
Still have questions about chemical filter selection or application? Contact us today for expert guidance, or explore our liquid filtration resources to learn more about the latest filtration technologies and industry trends.






 Air Filters
Air Filters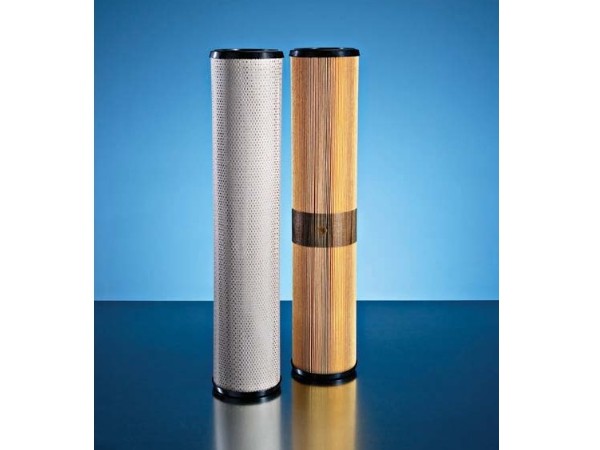 Liquid Filters
Liquid Filters Filtering Systems
Filtering Systems Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services